
Using the Savin and Ludwig scales to measure the rate and stage of androgenic alopecia in women
Hair loss occurs in around half of women by the age of 40. That figure rises to around two thirds of women by the age of 50. The most common type of hair loss is androgenic alopecia, also known as female (or male) pattern baldness.
The rate and activity of female pattern baldness is measured by using the Savin and Ludwig scales. If you are unfamiliar with this measurement process, then this article will explain everything you need to know about the Savin and Ludwig female hair loss measurement scales.
The Savin Scale
Savin hair loss, also known as Savin scale or Savin classification, is a method used to assess female pattern hair loss (FPHL). The Savin scale categorizes FPHL into three grades based on the severity of hair loss and the density of hair remaining on the scalp. The three grades are:
Grade I: Mild hair loss with preserved hair density in the affected area
Grade II: Moderate hair loss with decreased hair density in the affected area
Grade III: Severe hair loss with little to no hair remaining in the affected area
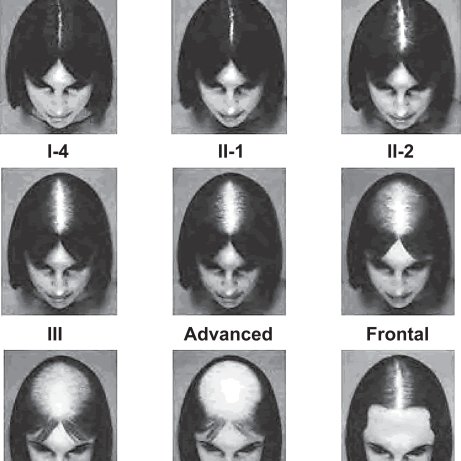
The Savin scale is often used by dermatologists and hair loss specialists to assess the degree of FPHL in their patients and to track changes in hair loss over time.
It is important to note that there are many potential causes of hair loss in women, and a proper diagnosis should be made by a healthcare professional before any treatment is pursued.
“Ludwig hair loss” is a term used to describe female pattern hair loss (FPHL) using the Ludwig classification system. The Ludwig classification system is another method of categorizing FPHL and is based on the pattern and degree of hair loss on the scalp.
The Ludwig Scale
The Ludwig Scale is very similar to the Savin Scale. The Ludwig classification system also divides FPHL into three grades:
Grade I: Mild hair thinning at the crown of the scalp
Grade II: Moderate hair thinning with a noticeable decrease in hair volume at the crown of the scalp
Grade III: Extensive hair thinning with only a rim of hair remaining along the front and sides of the scalp
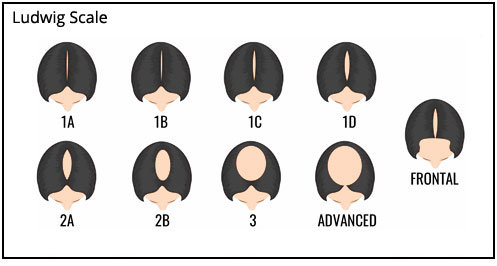
The Ludwig classification system is often used by dermatologists and hair loss specialists to assess the severity of FPHL and to monitor the progression of hair loss over time.
It is important to note that FPHL can have many causes, and a proper diagnosis should be made by a healthcare professional before any treatment is pursued.


Leave a Reply